
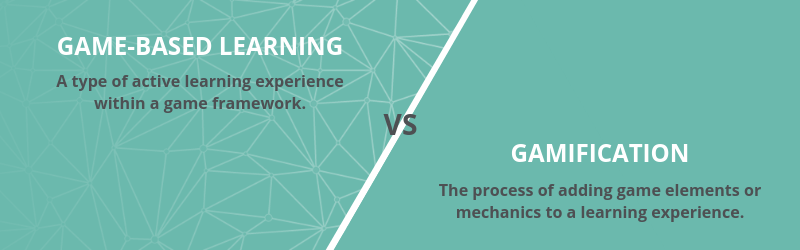
Game-based learning and gamification at immediate glance may seem like similar and interchangeable terms. While both terms combine games and learning, the difference lies in how game elements are integrated into the learning experience. This distinction leads to a larger difference in learning outcomes when comparing game-based learning vs. gamification.
A type of active learning experience within a game framework, which has specific learning objectives and measurable outcomes.
The learning experience gives a student clear and challenging goals within a virtual game framework, requires a high-degree of student interaction and offers informative feedback on student performance. Many times, the games are designed to allow the player to understand the subject matter within a real world context.
The process of adding game elements or mechanics to an experience to increase engagement or enjoyment.
These game elements are usually separated from the actual learning content. Gamified lessons or activities may include elements such as badges, leaderboards, timed activities, rewards or points.
Separating students into groups to compete on assignments or activities.
Enabling students to earn points for behavior or completion of assignments and allowing them to spend the points on rewards.
Timed flash cards or worksheets.
Badges to show completion of work or mastery of skills.
Listening for certain keywords or situations to complete a bingo-type sheet.
Using dice to generate random numbers for a worksheet activity.
In game-based learning, the game is the learning experience, whereas in gamification, the game components are added to the traditional instruction method.
In gamification, the end result (the points, rewards, being first place, completing as much as possible, not being last place) can easily become the focus, rather than the learning. Gamification can cause learners to rely on extrinsic motivation. This is the mental condition that drives a person to behave a certain way or engage in an activity to win a reward or avoid a punishment.
But what happens when the reward is no longer relevant or removed?
In addition, a number of studies have shown that offering excessive external rewards for an internally satisfying behavior can lead to a reduction in intrinsic motivation (Deci et al., 1999). Intrinsic motivation is a type of internal desire that is based on the satisfactions of behaving “for its own sake.”
If designed well, game-based learning has the capacity to harness students’ intrinsic motivation and love for play and lead them toward complex problem solving.
Research around game-based learning shows this correlation between motivation, engagement, complex problem solving and other social and emotional skills.
One of the more popular investigations is that of learning through failure and the shift from a fixed mindset to a growth mindset. A student with a fixed mindset believes that intelligence is inherent and unchanging. A student with a growth mindset believes that they can change and improve their knowledge with effortful learning (Carol Dweck, et al.)
The nature of learning through failure and mastery in games naturally lends itself to developing a growth mindset.
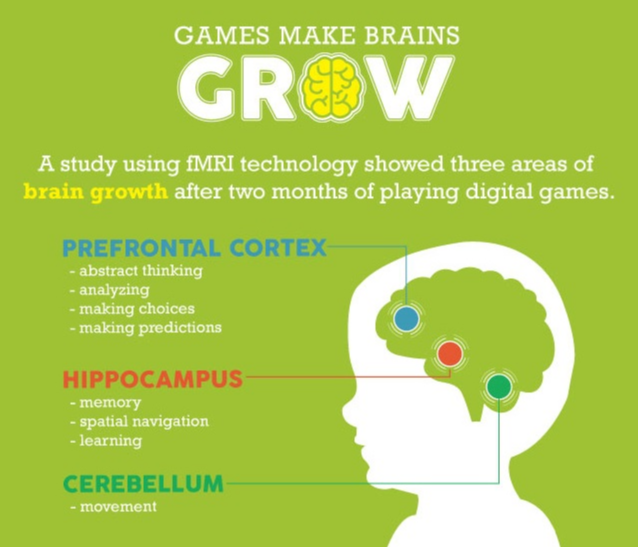
Explore more resources and research on the game-based learning infographic.
Making People Fail: Failing to Learn Through Games and Making
Level Up and Learning: A national survey on teaching with digital games
How are educators using this research to improve student outcomes in their classrooms?
Ryan Reed shares some game-based learning examples and how to help other educators get started with game-based learning.
With game-based learning, students become more engaged with their learning. They go from struggling to finding a way to overcome that struggle and start looking for solutions and innovating strategies on their learning.
-Ryan Reed, Business & Technology Teacher at Stillman Valley High School
In this video, MIND’s content director Ki Karou shares some game-based learning strategies that can develop students' capacity for productive struggle.
Video: Using Game-based Learning in the Classroom by MIND Research Institute

Calli Wright was the Marketing Manager at MIND Research Institute. She loves playing and designing board games, which she often talks about on twitter @CalliWrights.
Comment